The Importance of an Early Treatment with an Orthosis after a Stroke
A stroke is also called apoplexy, brain attack or cerebrovascular accident. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), around 15 million people worldwide suffer a stroke every year. As a stroke usually occurs regionally in one half of the brain, the consequence is often hemiplegia or hemiparesis.
Quick Action in the Acute Phase
If it is not possible to stand and walk safely in the early phase, so-called acute phase, of a stroke, e.g. due to paralysis, early mobilisation by means of an orthosis is recommended to influence the course of therapy as positively as possible. Currently, the supply of medical devices in the acute phase often does not include an orthosis, as the support that the right orthosis can provide when standing is underestimated. A physical examination using visual or instrumental gait analysis as well as the assessment of the gait can only take place when the patient is secure enough for gait training. As a result, the physical examination often takes place too late and the therapeutic effect that can be achieved with the help of the right orthosis during stance training is missed. Since gait training often occurs long after the first standing exercises, post-stroke patients with hemiplegia often receive the right orthosis too late. To close this gap, we have developed a suggestion on how a treatment with the right orthosis can already be integrated into stance training.
Depending on the therapy status, there are three options for the physical examination:

- In the acute phase: Early mobilisation while still in the hospital should always be aimed for if possible.
- For later treatments: A physical examination using visual or instrumental gait analysis is the standard approach when safe stance and gait are already possible.
- In individual cases, e.g. in the case of severe shortening (contractures) in the ankle, knee or hip: Carrying out the physical examination including a muscle function test. In combination with another indication involving instability of the knee, the configuration of a KAFO may become necessary.
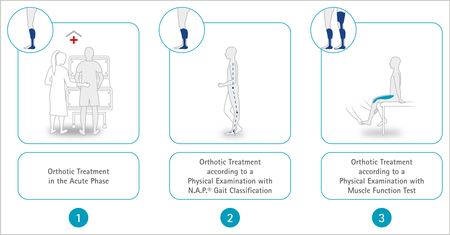
The FIOR & GENTZ Orthosis Configurator offers a configuration path for all three cases. The circles at the top left of the graphics show the proper treatment when choosing the respective configuration path.
Why an Orthosis Helps
If certain neuronal functions have been lost due to a stroke, these can be taken over by unaffected areas of the brain. This process of creating new nerve connections is called neuronal plasticity. The trigger for this process is the repeated training of the impaired functions, which should start as soon as possible after the stroke. In particular, if neuronal functions are impaired that are responsible for balance and muscles for safe standing and walking, both stance and gait training must be started very early.
Stance Training as Preparation for Gait Training
Before walking comes standing. Even though standing still is perceived as a simple motor task, it involves the same muscle groups as walking. Find out more about this in the section on Paralyses and Orthoses and also how paralysis of the calf muscles (plantar flexors) affects stance and gait.
Dynamic orthoses are a valuable support for a safe stance after a stroke and can prevent or reduce the appearance of spastic pareses. Although the patient might not be able to put on the orthosis himself, stance training should already begin in the acute phase. This early stance training offers the following advantages:
- Regaining the balance and sense of balance is supported.
- Bringing the body into an upright position (verticalisation) has a variety of positive effects on the human organism.
- The controlled load on the muscles prevents the shrinking (atrophy) of the muscles and can shorten the time to regain independent walking.
- The risk of shortening (contractures) in the knee and hip due to lying or continuous sitting in a wheelchair is reduced.
- Furthermore, it supports the prevention of pes equinus as the muscles are stretched and loaded dynamically. The orthosis prevents the foot from staying in a permanent pes equinus position when lying in bed.
Without an orthosis, training can be very laborious for both the therapist and the patient. A custom-made initial orthosis can be produced for the affected leg in the acute phase already and subsequently adapted to the gait, provided that it has been built correctly and with the correct system joint right from the start. In combination with a subsequent physiotherapy/occupational therapy, this helps the patient regain security and confidence during stance and gait. Unfortunately, the importance and potential of the right orthosis for the course of therapy is often underestimated or not even recognised.
In most cases, it makes sense to provide the patient with a custom-made ankle-foot orthosis. Such an orthosis is also called AFO. The term AFO (ankle-foot orthosis) refers to the body parts included in the orthotic treatment: ankle and foot.
An orthosis with individual functional elements affects different levels:
- support of the paralysed calf muscles (plantar flexors) for more safety while standing and walking
- support of the paralysed shin muscles (dorsiflexors) to prevent tripping
- balance support thanks to functional elements with precompressed spring units
Through these three functions, the orthosis helps the muscles establish the correct cerebral connections through motor impulses. A cerebral connection is the control programme that the brain stores in order to be able to execute complex movement patterns.
Concept for the Treatment with an Orthosis after a Stroke
Our Stroke Guide offers “a concept for the orthotic treatment of the lower extremity following a cerebral vascular accident”. It contains various orthotic treatment suggestions for the different gait types after a stroke.
The basis for the division of the gait types is the N.A.P. Gait Classification®. It was developed by physiotherapists and experts from the fields of orthopaedic technology and medicine to facilitate interdisciplinary communication and treatment selection. The guide describes recommendations for orthotic treatments as well as their effect and how they differ from previous treatment options.
You can download the Stroke Guide free of charge here. Upon request, we will gladly send you a printed copy. Please contact our In-house Customer Service at info(at)fior-gentz.de or +49 4131 24445-0.
You will find an overview of the different system joints in the knee and ankle area here. The most important functions of the respective system joint are explained in the corresponding product description.
You can get to know patients who have already been treated with an orthosis in our User Stories and Patient Videos. You will find the section on patients with stroke here.
General Information on Strokes
What Is a Stroke?
A stroke is the result of a sudden circulatory disorder in the brain. The brain is undersupplied for more than 24 hours, which can lead to cells dying. The affected areas of the brain can no longer fulfil their task properly.
There are two main types of stroke:
Ischaemic Stroke (Most Common Type of Stroke)
reduced blood flow and thus undersupply of an area
Haemorrhagic Infarction/Stroke
acute cerebral bleeding, causing areas to become undersupplied as blood flows into surrounding tissues
What Are the Symptoms of a Stroke?
The FAST test (Face, Arms, Speech, Time) can be used to quickly confirm the suspicion of a stroke.
F (Face) Can the person smile without one side of the face becoming distorted?
A (Arms) Can the person stretch both arms forward and turn their palms upward?
S (Speech) Can the person repeat a simple sentence?
T (Time) If all symptoms occur, do not waste time. Call the emergency services!
What Are the Consequences of a Stroke?
Different impairments can occur depending on which area of the brain is affected. Some of them remain permanently. This includes:
- difficulties when speaking
- impaired vision
- motor function restrictions
- paralysis of arms and/or legs
- difficulties when walking
What is a TIA?
A TIA (Transient Ischaemic Attack) is a so-called mini stroke. A circulatory disorder occurs here as well. However, the symptoms disappear within 24 hours.
A TIA may be a warning sign of an impending stroke. The causes and symptoms are the same. Even if the symptoms disappear, one should urgently consult a physician.


